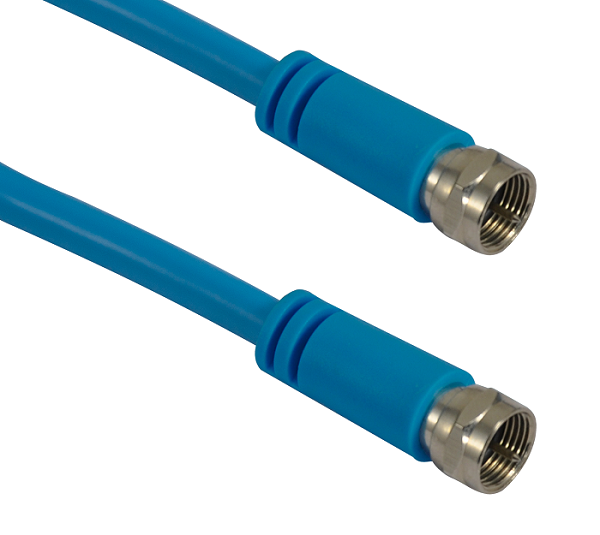
The growth of wireless and high-speed data applications has caused the use
of coaxial cables to surpass traditional video and telecommunications cables.
With the development and standardization of coaxial cables used in various
applications, coaxial cables have become common equipment in homes, offices,
telecommunications facilities, railways, industrial plants, and
government/public safety facilities. The diversification of such applications
has led to diversification of the types, grades and manufacturers of coaxial
cables.
Coaxial cable application requirements and parameters
The beginning of everything is always to understand the problem to be
solved. For the purchase of coaxial cable, this means that you need to know the
quality of the signal that the cable needs to carry. Some of the important
factors are the frequency range and the power level of the transmitted signal.
Other factors include the radio frequency and electromagnetic environment
through which the signal passes, wiring length, and wiring difficulty. Around
the specific coaxial cable selected for a certain application, the project
budget and all institutional requirements also play an important role in
decision-making.
1. Correctly select impedance
The two main impedances used in coaxial cables are 75 ohms and 50 ohms.
Unless there is a visible marking content, the impedance of a coaxial cable
cannot be judged from the outside. If the above two impedances are confused, it
may cause damage to the device connector or the device itself, or at least
degrade system performance. Although sometimes used crosswise, 75-ohm cables are
often used for video applications, while 50-ohm cables are more commonly used
for data and wireless purposes. The type of equipment and device to be connected
determines the cable impedance to be used.
2. Correctly select the cable length according to the attenuation
Signal energy can be lost due to thermal energy caused by conductor
resistance, dielectric loss factor and other factors related to the quality of
the coaxial cable material. The attenuation of a coaxial cable represents the
energy loss per unit length of the cable. For applications where the signal
power is extremely low or the wiring requirements are extremely long, and there
is no amplifier or signal booster, a low-loss cable may be required to meet the
minimum signal strength requirements at the receiving end of the coaxial cable.
If the attenuation of the coaxial cable is so low that there is no need to use a
signal booster, even if the price of the low-loss cable is more expensive, the
use of the cable is still a cost-effective investment.
Different cables have different power ratings
Depends on the cable diameter, the type of central and outer conductors,
and the quality of the cable. Different cables have different rated maximum
processing powers. These ratings are given in the form of values under
continuous wave conditions, average values or peak values, and have different
meanings depending on the type of signal carried. In addition, it is possible to
give the rated values of the rated maximum voltage and the rated maximum
current. It should be noted that such ratings also depend on the frequency, and
cables with better safety margins should be selected. Once the rated power of
the coaxial cable is exceeded, there is a risk of unfortunate failure modes such
as electric sparks, accelerated aging, medium degradation, and combustion.
Not all coaxial cables have the same shielding performance
Coaxial cables have a variety of structure types such as braided, stranded,
foil, solid, corrugated, etc., a variety of outer conductor types, and a variety
of shielding methods. In order to further reduce the interference received or
emitted, some coaxial cables can have multiple shielding layers in addition to
the outer conductor. In addition, the use of different types of outer conductors
and shielding layers can also achieve crush resistance, higher
rigidity/flexibility and lower attenuation. For many applications, when budget
allows, the higher the quality of the outer conductor and shielding layer of a
coaxial cable, the better, and the more the number, the better.
How to wire/route?
Different applications usually have very different wiring requirements. The
wiring requirements for large outdoor industrial environments are different from
those in machinery facilities or aircraft fuselages. From wiring in equipment
assemblies to wiring in complex buildings, for almost any environment, there is
a corresponding coaxial cable that can meet its needs. For specific wiring
types, coaxial cables have several technical parameters to measure whether they
can meet the requirements, including: bending radius, maximum load or
unsupported wiring conditions, wind load, and a variety of environmental factors
and ratings. Normally, such information should be provided to the cable
purchaser, otherwise the exact details of the wiring requirements may be as
important as the electrical performance of the cable. Because some applications
make the wiring operation rougher, different sheath materials and protective
layers are usually used to assist in cable installation.
What type of connector do I need?
When using non-dedicated coaxial connectors, some coaxial cables may have
problems with oversize or undersize. Many manufacturers provide optimized
coaxial connectors for specific cables, and low PIM or low loss applications
require the use of dedicated high-performance connectors. In addition, the
coaxial connector and the cable can be connected by crimping, welding, and
toolless press-fitting. One thing to consider is that not all cables are
suitable for certain connection types.
Should I buy a coaxial cable or a coaxial cable assembly?
Due to the diversity and application requirements of coaxial connectors and
cables during installation, many suppliers provide pre-assembled coaxial
components for specific purposes. For a specific application, if the cable
length, performance parameters, and coaxial connector type are known, then the
best choice is to use cable assemblies.
Institutional requirements and special equipment
Certain applications, such as military, government, avionics, aerospace and
industrial equipment, have specific regulations and requirements for coaxial
cable performance. Only by meeting the institutional requirements of these
industries, society, and governments, can cables be qualified to be used in
these fields. These requirements can be quite complex, and it is not easy to
remember them. Experts may be the best candidates for details here.
Special cable
Many special applications such as test and measurement, scientific
experiments, satellites, high-performance radars, etc. require the use of very
special coaxial cables. In addition to the above-mentioned institutional
standards, these cables usually need to meet specific applications and many
non-standard requirements. Experts can help purchasers understand the cables
that can meet specific needs one by one, and finally choose the best option.
Counterfeit cables and counterfeit goods
Unfortunately, due to profit-driven, counterfeit coaxial cables sold
illegally are more accessible to the buying crowd. The use of cables other than
genuine ones is illegal in itself and may put the safety of operators and
equipment at risk. Only choosing qualified suppliers with good historical
records and quality management systems is the best measure to prevent potential
losses caused by counterfeit coaxial cables.
 English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Català
Català  שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Cymraeg
Cymraeg  Galego
Galego  Latviešu
Latviešu  icelandic
icelandic  ייִדיש
ייִדיש  беларускі
беларускі  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen  Shqiptar
Shqiptar  Malti
Malti  lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  Bosanski
Bosanski  Frysk
Frysk  ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ  ქართული
ქართული  ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી  Hausa
Hausa  Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили  ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ  Corsa
Corsa  Kurdî
Kurdî  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Maori
Maori  Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл  Hmong
Hmong  IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa  Zulu
Zulu  Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch  Malagasy
Malagasy  Punjabi
Punjabi  پښتو
پښتو  Chichewa
Chichewa  Samoa
Samoa  Sesotho
Sesotho  සිංහල
සිංහල  Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig  Cebuano
Cebuano  Somali
Somali  Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ  O'zbek
O'zbek  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  سنڌي
سنڌي  Shinra
Shinra  Shinra
Shinra  Հայերեն
Հայերեն  Igbo
Igbo  Sundanese
Sundanese  Yoruba
Yoruba  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Az?rbaycan
Az?rbaycan  Slovensky jazyk
Slovensky jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик