What is the difference between CAT5E, CAT6 and CAT6A in system performance and network applications?
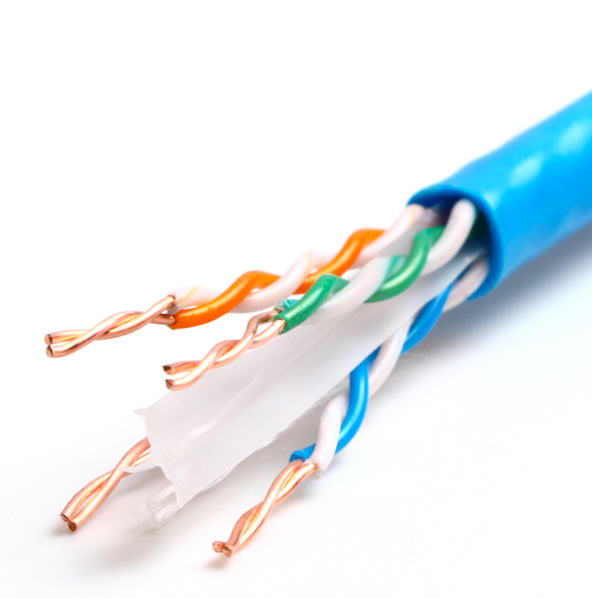
1. CAT5E wiring physical bandwidth: 100MHz, CAT6 wiring physical bandwidth: 250MHz;
Description: The larger the physical bandwidth, the higher the transmission rate supported.
2. CAT5E Cables usually use 24AWG wire gauge (about copper core diameter: 0.51mm), and CAT6 cables usually use 23AWG wire gauge (copper core diameter about 0.57mm);
Description: The thicker the copper core diameter, the better the conduction performance, and the smaller the signal attenuation on the line. In PoE applications, 23AWG has an absolute advantage over 24AWG in energy transfer.
3. The maximum data transmission rate supported by CAT5E wiring theory is 1200Mbps, and the maximum data transmission rate supported by CAT6 wiring theory is 2400Mbps;
Description: The higher the data transfer rate, the larger the physical bandwidth.
4. The 10GBASE-T 10G Ethernet application standard that CAT5E wiring does not support, and the 10GBASE-T Ethernet application standard that CAT6 wiring can support, but the transmission distance is limited and cannot exceed 37 meters.
Description: Category 6 cabling system can barely meet the application requirements of 10 Gigabit Ethernet over short distances, while Category 5 systems cannot support it.
5. CAT6 cables usually adopt a cross frame structure to reduce crosstalk between pairs. Its (NEXT) near-end crosstalk performance index is 5-10dB higher than that of CAT5E without a frame structure (1-100MHz);
Description: Minimizing crosstalk between pairs is the most important basic prerequisite for the stable and high-speed transmission of data information in a wiring system.
Comprehensively compare the differences between the above-mentioned two levels of wiring systems, the Category 6 wiring system is not only far higher than the Category 5 cabling system in terms of physical and electrical performance, but also much higher than the Category 5 wiring system in terms of high-speed and stable data transmission. At the same time, as the category 6 cabling market continues to mature, the large-scale promotion of category 6 products drives the production of large-scale category 6 products, making the price of category 6 wiring products no longer much higher than the price of over 5 categories.
What is the difference between CAT5E, CAT6 and CAT6A in system performance and network applications?
Next, here is a brief description of the difference in product performance between CAT6 and CAT6A cabling systems:
1. CAT6 wiring physical bandwidth: 250MHz, CAT6A wiring physical bandwidth: 500MHz;
Description: The larger the physical bandwidth, the higher the transmission rate supported.
2. CAT6 cable loop resistance (at 20℃) 155 ohm/km, NVP value: 69%;
CAT6A cable loop resistance (at 20°C) 150 ohm/km, NVP value: 76%;
Description: The smaller the copper core loop resistance, the better the conduction performance, and the smaller the signal attenuation on the line. The cable NVP value is the percentage of the electrical signal transmission rate in the copper medium equivalent to the speed of light in vacuum. The higher the NVP value, the faster the transmission speed of the electronic signal in the medium.
3. The 10GBASE-T 10 Gigabit Ethernet application standard supported by CAT6 cabling, but the transmission distance is limited, not exceeding 37 meters (and the need to increase the external crosstalk test to re-evaluate the performance of the Category 6 cabling system against external electromagnetic interference). CAT6A cabling can support the 10GBASE-T Ethernet application standard, which meets the 100-meter range standard application without additional external crosstalk testing.
Description: The CAT6A cabling system can fully meet the application requirements of 10 Gigabit Ethernet at a distance of 100 meters, and there are many defects in the transmission of 10 Gigabit Ethernet by the CAT6 cabling system.
4. CAT6A cable usually adopts the method of aluminum foil shielding and aluminum foil total shielding to achieve extremely good shielding effect against external electromagnetic interference and crosstalk between pairs. The crosstalk between the six types of unshielded twisted pairs of the cross frame structure is 15-35dB higher in the range of (1-250MHz).
Description: Minimizing crosstalk between pairs and avoiding external electromagnetic interference from cables are the most important basic premise for the stable and high-speed transmission of data information in a wiring system.
The integrated wiring system has been developed for more than 20 years. With the popularization of network applications in various fields, the number of ports has increased sharply. And with the continuous development of information technology, users have higher and higher requirements for network speed. In order to support the development of network speed, the network cabling system has also been extended from the initial three types of systems to today’s support for 10 Gigabit transmission. CAT6A (Cat 6), can provide a horizontal transmission rate of 10 Gigabits and 10Gbps. So for now, the transmission performance of copper cabling is no longer an application bottleneck.
 English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Català
Català  שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Cymraeg
Cymraeg  Galego
Galego  Latviešu
Latviešu  icelandic
icelandic  ייִדיש
ייִדיש  беларускі
беларускі  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen  Shqiptar
Shqiptar  Malti
Malti  lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  Bosanski
Bosanski  Frysk
Frysk  ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ  ქართული
ქართული  ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી  Hausa
Hausa  Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили  ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ  Corsa
Corsa  Kurdî
Kurdî  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Maori
Maori  Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл  Hmong
Hmong  IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa  Zulu
Zulu  Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch  Malagasy
Malagasy  Punjabi
Punjabi  پښتو
پښتو  Chichewa
Chichewa  Samoa
Samoa  Sesotho
Sesotho  සිංහල
සිංහල  Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig  Cebuano
Cebuano  Somali
Somali  Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ  O'zbek
O'zbek  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  سنڌي
سنڌي  Shinra
Shinra  Shinra
Shinra  Հայերեն
Հայերեն  Igbo
Igbo  Sundanese
Sundanese  Yoruba
Yoruba  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Az?rbaycan
Az?rbaycan  Slovensky jazyk
Slovensky jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик